
OFFSHORE ENGINEERING, DESIGN & CONSTRUCTION
Sustainable Power: The Renewable Energy Revolution
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources, which are naturally replenished on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. Renewable energy often provides energy in four important areas: electricity generation, air and water heating/cooling, transportation, and rural (off-grid) energy services.
Renewable energy resources exist over wide geographical areas, in contrast to other energy sources, which are concentrated in a limited number of countries. Rapid deployment of renewable energy and energy efficiency is resulting in significant energy security, climate change mitigation, and economic benefits. The results of a recent review of literature concluded that as greenhouse gas (GHG) emitters begin to be held liable for damages resulting from GHG emissions resulting in extreme climate change. Some places and at least two countries, Iceland and Norway generate all their electricity using renewable energy already.



Displacing Fossil Fuels in Three Key Areas

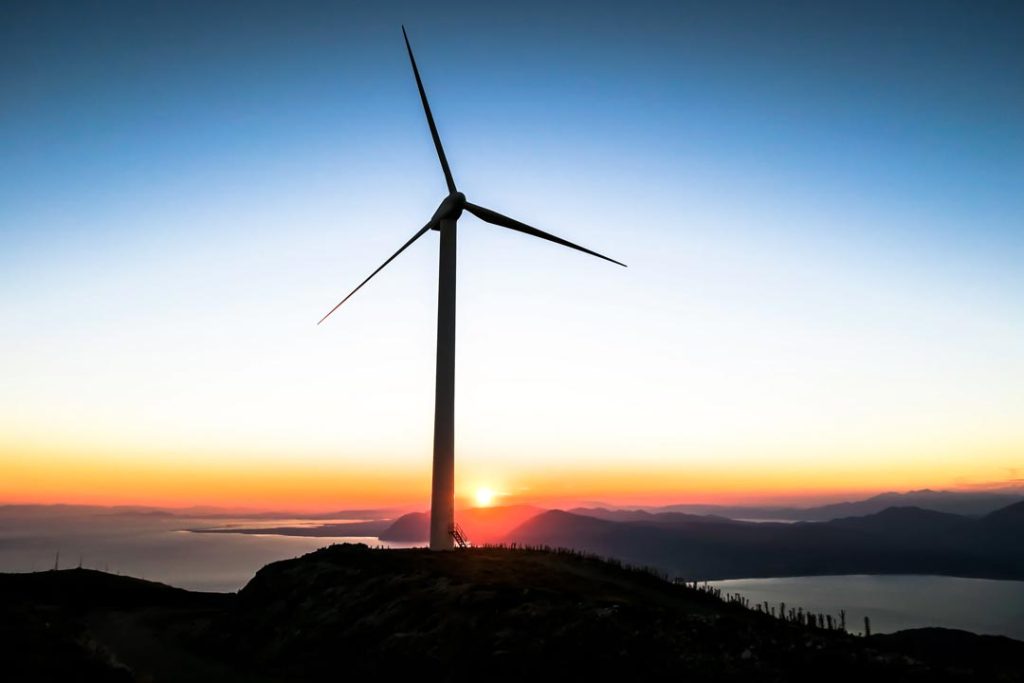
Power Generation
By 2040, renewable energy is projected to equal coal and natural gas electricity generation. Several jurisdictions, including Denmark, Germany, the state of South Australia and some US states have achieved high integration of variable renewables. For example, in 2015 wind power met 42% of electricity demand in Denmark, 23.2% in Portugal and 15.5% in Uruguay. Interconnectors enable countries to balance electricity systems by allowing the import and export of renewable energy.


Power Generation
By 2040, renewable energy is projected to equal coal and natural gas electricity generation. Several jurisdictions, including Denmark, Germany, the state of South Australia and some US states have achieved high integration of variable renewables. For example, in 2015 wind power met 42% of electricity demand in Denmark, 23.2% in Portugal and 15.5% in Uruguay. Interconnectors enable countries to balance electricity systems by allowing the import and export of renewable energy.


Power Generation
By 2040, renewable energy is projected to equal coal and natural gas electricity generation. Several jurisdictions, including Denmark, Germany, the state of South Australia and some US states have achieved high integration of variable renewables. For example, in 2015 wind power met 42% of electricity demand in Denmark, 23.2% in Portugal and 15.5% in Uruguay. Interconnectors enable countries to balance electricity systems by allowing the import and export of renewable energy.